The Science-Based Targets initiative (SBTi) is a collaborative effort between CDP, the United Nations Global Compact, World Resources Institute (WRI), and the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) that aims to empower organizations in the private sector to set science-based emissions reduction targets. By providing companies with a clearly-defined path aligned with the goals of the Paris Agreement, science-based targets enable businesses to contribute to the fight against climate change. With over 4,000 businesses already engaged in the initiative, the SBTi plays a critical role in accelerating climate action worldwide.
Read moreMalaysia’s country-specific GHG Emission Factors
According to Bank Negara Malaysia (BNM), Malaysia is planning to create its own greenhouse gas (GHG) emission factors* tailored to the country’s key sectors. The purpose of this initiative is to support the implementation of a carbon price framework.
Read moreRace to Zero campaign
The Race to Zero is a global campaign aligned with the Paris Agreement, aiming to mobilize non-state actors to take ambitious action on climate change. It seeks to achieve net-zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 2050 at the latest. The campaign recognizes that governments alone cannot tackle the climate crisis and requires action from businesses, cities, regions, investors, and other organizations.
Read moreEcovadis: Sustainability Assessment
Ecovadis is a global leader in sustainability ratings and assessments, providing businesses with a comprehensive evaluation of their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance. The company’s assessment methodology is based on a holistic approach that evaluates companies across 21 sustainability criteria, grouped into four themes: Environment, Labor & Human Rights, Ethics, and Sustainable Procurement.
Read moreThe Chief Sustainability Officers’ (CSOs) responsibilities.
Sustainable development management
Sustainable development management is the practice of integrating sustainable principles into business operations and decision-making processes. It involves identifying and managing environmental and social risks, setting sustainability goals and targets, measuring and reporting on sustainability performance, and promoting innovation and collaboration to drive sustainability improvements. This approach aims to create long-term value for the business, society, and the environment while minimizing negative impacts and risks.
Read moreCarbon Neutrality and Net Zero Emissions
Carbon neutrality and net zero emissions are two terms that are often used interchangeably, but there are some important differences between them. Carbon neutral organizations evaluate and reduce CO2 emissions and compensate for them by reducing emissions elsewhere or removing CO2 from the atmosphere through carbon offsetting. Net Zero means a company reduces absolute emissions across its whole supply chain to limit global temperature increases. The Science Based Targets initiative has set out the world’s first Net Zero standard. Both terms are essential parts of emissions mitigation work to combat climate change.
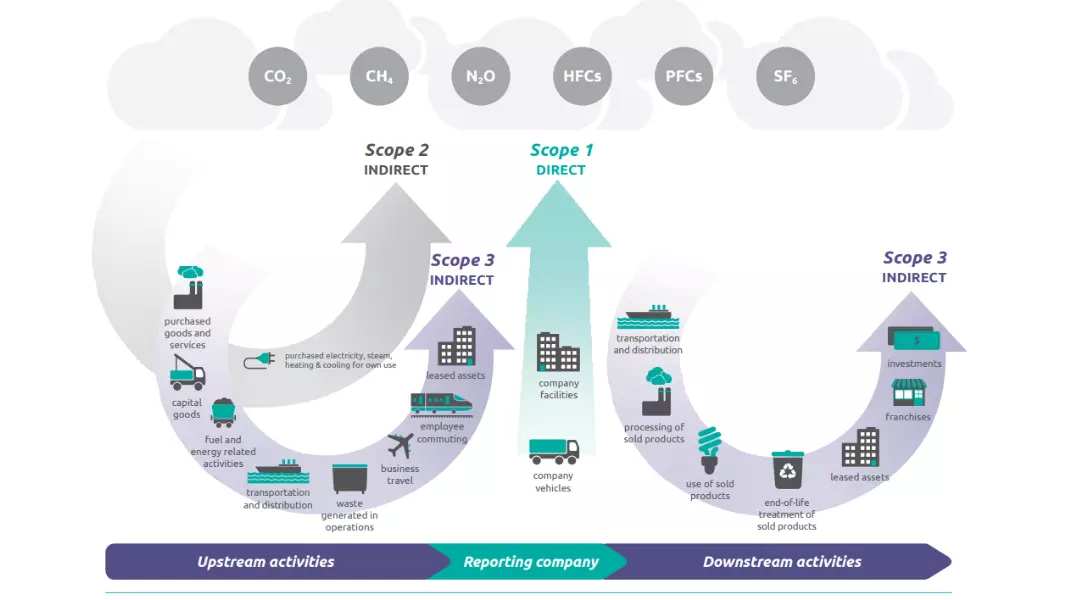
Read moreDirect and indirect greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions can be categorized as direct emissions or indirect emissions.
Direct GHG emissions (also known as Scope 1 emissions in the GHG Protocol) are emissions that are produced directly by sources that are owned or controlled by an organization. Examples of direct GHG emissions include emissions from combustion of fuels in boilers or vehicles owned by the organization, and emissions from chemical processes in manufacturing facilities.
Read moreThe GHG Protocol Corporate Accounting and Reporting Standard
The GHG Protocol Corporate Accounting and Reporting Standard (the GHG Protocol) is a widely recognized framework for companies to measure and manage their greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. It was developed by the World Resources Institute (WRI) and the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD), and it provides a consistent and transparent method for companies to quantify and report their GHG emissions, as well as to identify opportunities to reduce those emissions.
Global warming potential (GWP) of greenhouse gases.
Different greenhouse gases have different warming potentials, meaning that they trap different amounts of heat in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) is a metric used to compare the emissions from various greenhouse gases (GHGs) based on their potential to contribute to global warming.
Read moreGreenhouse gases (GHGs)
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are gases that trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere and contribute to global warming and climate change. They act like a blanket around the Earth, trapping heat that would otherwise escape into space. Some examples of GHGs include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide.
Read more